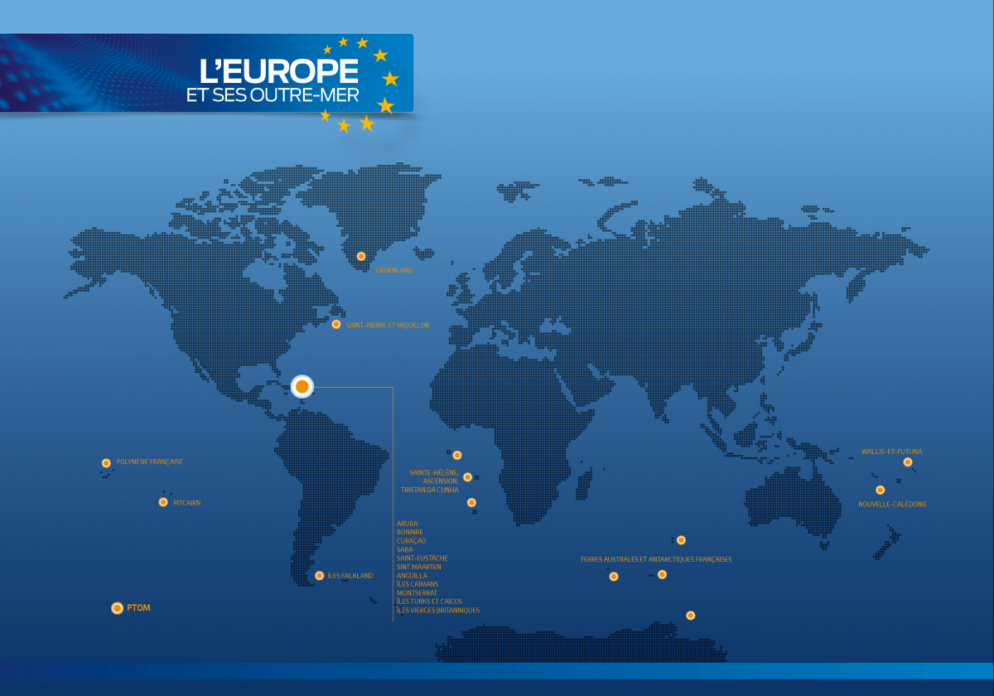
Who are the OCTs?
The OCTs -25 countries and territories - have constitutional links with Denmark (DK), France (FR), the Netherlands (NL) and the United Kingdom (UK). Although their nationals are generally European citizens, these territories are not part of the European Union and are not directly subject to European law. OCTs benefit from a special “associated” status within the European Union, defined to foster their economic and social development.
In detail
OCTs are :
• Anguilla (UK)
• Aruba (NL)
• Bermuda (UK)*
• Bonaire (NL)
• British Antarctic Territory (UK)**
• British Indian Ocean Territory (UK)**
• British Virgin Islands (UK)
• Cayman Islands (UK)
• Curacao (NL)
• Falkland Islands (UK)
• French Polynesia (FR)
• French Southern and Antarctic Territories (FR)**
• Greenland (DK) • Montserrat (UK)
• New Caledonia (FR)
• Pitcairn Islands (UK) • Saba (NL)
• Saint-Barthélemy (FR)
• Sint Eustatius (NL)
• Sint-Maarten (NL)
• South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (UK)**
• Saint Helena, Ascension Island, Tristan da Cunha (UK)
• Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelon (FR)
• Turks and Caicos Islands (UK)
• Wallis-et-Futuna (FR)
(*) Bermuda applies the new regime since 1/1/2014.
(**) OCTs, without a permanent local population.